|
KERALA AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
|
TUBERS
Elephant foot yam (Amorphophallus paeoniifolius)
Elephant foot yam requires fairly
long growing season and a rainfall of about 150 cm during the crop period. A
well-drained soil of medium texture is suited for this crop.
Season
Corm pieces are normally planted
during February-March, before the onset of monsoon.
Variety
Sree Padma: The crop matures in 8-9
months. Cooked tubers are free from acridity.
Sree Athira; First genetically
improved variety with very good cooking quality.
Seeds and sowing
Tuber cut-pieces weighing about 1 kg
are ideal for planting. Dip the pieces in cowdung slurry and allow to dry under shade
before planting. Nematodes associated with amorphophallus can be controlled by
seed material treatment with talc based
formulation of Bacillus macerans @ 3g
(106 cfu/g) per kg of corms. After planting, cover the
pit with dried leaves or other mulching materials. About 12,000 cut pieces weighing about 12
t are required for planting one hectare. Most of the seed material will germinate within
one month after planting.
Mealy bugs usually attack the corm
in field and store. Avoid planting corms already infested.
Land Preparation
Dig pits of 60 cm x 60 cm x 45 cm
size 90 cm apart. Collect the topsoil to a depth
of 15-20 cm separately and fill it after the pits are formed. Apply cowdung or compost
at 2-2.5 kg/pit and mix with topsoil.
Minisett technique for quality
planting materials
Minisetts weighing 100 g each can
be planted directly in nursery beds or in the main field with the central bud portion facing up
at a spacing of 60 cm x 45 cm. A total of 37,000 minisetts/ha is required as against 12,345
setts/ha in the traditional method.
Multiplication ratio in elephant foot yamcould be
enhanced to 1:15 as against the conventional 1:3
by adopting minisett technique.
After cultivation
Apply full dose of
P2O5 and half the dose N and
K2O
(N:P2O5:K2O @ 50:50:75 kg
ha-1) after forty five days of planting along with intercultivation and weeding. Apply
second dose of fertilizers (N and K2O @ 50:75
kg ha-1) one month after the first application along with intercultivation and earthing up.
Harvesting
The crop will be ready for harvest 8-9 months after planting.
Organic farming technology for
elephant foot yam
Recommendation
• Raising green manure cowpea (seed
rate @ 20 kg ha-1) prior to elephant foot yam and incorporation of green matter at
45-60 days.
• Use of organically produced
planting materials.
• Treatment of corm pieces of 500-750
g with slurry containing cowdung, neem cake and
Trichoderma harzianum (5 g/kg seed) and drying under shade
before planting.
• Application of
Trichoderma harzianum incorporated FYM @ 36 t
ha-1 (3 kg/pit) in pits at the time of planting (FYM neem
cake mixture (10:1) inoculated
with Trichoderma harzianum @ 2.5 kg/tonne of FYM neem cake mixture. Trichoderma
can be multiplied in FYM alone but it will take 15 days to form sufficient inoculam
as against 7-8 days if neem cake is also used along with FYM). This is effective
against collar rot caused by Sclerotium
rolfsii.
• Application of neem cake @ l.0 t
ha-1
(80-85 g/pit) in pits at the time of planting.
• Inter-sowing of green manure
cowpea (seed rate @ 20 kg ha-1 )
between elephant foot yam pits and incorporation of green matter in pits a i 45-60
days. The green matter addition from the 2 green manure crops should be
20-25 t ha-1.
• Application of ash @ 3 t
ha-1 (250 g/pit) at the time of incorporation of
green maure in pits.
COLOCASIA [TARO] (Colocasia
esculenta)
Colocasia is a crop of tropical and sub-tropical regions and requires a warm humid climate. Under rainfed conditions, it requires a fairly well distributed rainfall around 120-150 cm during the growth period. Well-drained soil is suitable for uniform development of tubers.
Season
Rainfed crop : May-June to Oct-Nov.
Irrigated crop : Throughout the year
Varieties
Sree Rashmi, Sree Pallavi and
Sreekiran are three improved varieties.
Sree Rashmi - Economic yield under
low input levels, conical cormets and 7 months duration.
Sree Pallavi - Field tolerant to leaf blight
and mosaic, club shape cormets and 7 months duration.
Sreekiran - First hybrid taro variety in India, long keeping quality
of cormets and 61/2 - 7
months duration.
Seeds and sowing
Use side tubers each of 25-35 g for
planting. About 37,000 side tubers weighing about
1200 kg are required to plant one hectare.
Plough or dig the land to a depth of
20-25 cm and bring to a fine tilth. Make
ridges 60 cm apart. Plant the side corms at a spacing of 45 cm on the ridges.
Manuring
Apply cattle manure or compost @ 12
t ha-1 as basal dressing, while preparing the ridges for planting. A fertilizer dose
of 80:25:100 kg of
N:P2O5:K2O per ha
is recommended. Full dose of
P2O5 and half dose of N and
K2O should be applied within a week after sprouting and the remaining
half dose of N and K2O one month after the
first application along with weeding and earthing up.
Aftercultivation Irrigation
Ensure sufficient moisture in the soil
at the time of planting. For uniform sprouting, irrigate just after planting and one week
later. Subsequent irrigation may be given at
12-15 days intervals, depending on
the moisture retention capacity of the soil. The irrigation should be stopped 3-4 weeks
before harvest. About 9-12 irrigations are
required for the crop till harvest. In the case of
rainfed crop, if there is prolonged drought, supplementary irrigation is required.
Inter-cultivation is essential in colocasia. Weeding, light hoeing and earthing up
are required at 30-45 days and 60-75 days after planting. The leafy parts may be
smothered about one month before harvest so as to enhance tuber development.
Mulching
Soon after planting, cover the ridges
with suitable mulching materials for retention of moisture and to control weeds.
Plant protection
Colocasia blight can be controlled
by spraying zineb, mancozeb or copper oxychloride formulations at 2 g
l-1of water (1 kg ha-1). For controlling serious
infestation of aphids, apply dimethoate at 0.05 per
cent. Leaf feeders can be controlled by applying malathion or carbaryl.
Harvesting
Colocasia becomes ready for harvest five to six months after planting. The
mother corms and side tubers are separated after harvest.
Storage of seed material
The side tubers to be used as
planting materials are usually separated from the mother corm and stored. Keep seed tuber
in sand spread over the floor to avoid rotting.
1. GREATER YAM (Dioscorea alata)
Greater yam is predominantly a
tropical plant. The crop cannot withstand frost
and excessively high temperatures. Temperature around 30ºC and rainfall of 120-200
cm distributed throughout the growth period are ideal. Day length greater than 12 hours
during initial stages and shorter day length
during the later part of the growing season favour satisfactory tuber formation. Yam
requires loose, deep, well-drained, fertile soil.
The crop does not come up well in waterlogged conditions.
Season
Seed tubers are normally planted during the later part of the dry season (March-April) and start sprouting with the onset of pre-monsoon showers. If the planting is delayed, yams start sprouting in storage, which is not desirable for planting.
Varieties
1. Sree Keerthi: Suitable for
intercropping in mature coconut garden and with banana. 3. Indu: This is recommended as a pure
crop and also as an intercrop of coconut in the reclaimed alluvial soils of Kuttanad.
4. Sree Shilpa: This is the first hybrid
having good culinary quality. The crop matures early, within 8 months. The tubers
have 33-35 per cent dry matter, 17-19 per cent starch, 1.4-2 per cent protein and 0.8-1.2 per cent sugar.
5. Sree Karthika : High yiled,
excellent cooking quality. The crop matures within 9 months. The tubers have 21.42 per
cent starch, 1.14 per cent sugar and 2.47 per cent crude protein. Seeds and sowing
D. alata produces mostly a single
big tuber in which only one head end of the tuber is available as good seed material. For
getting the head end in each propagation unit, the whole tuber is divided longitudinally.
Each piece of cut tuber should weigh at least
250-300 g. Dip the pieces in cowdung
slurry and allow to dry under the shade before planting. About 2500-3000 kg of seed
material is required to cover one hectare of land.
2. Sree Roopa: Possesses excellent cooking quality.
Preparation of land
Plough or dig the land up to a depth
of 15-20 cm. Dig pits of size 45 x 45 x 45 cm at a distance of 1 x 1m. Fill up three fourth
of the pits with 1-1.25 kg cattle manure or compost and mix with topsoil. Plant the cut
tuber pieces and completely cover the
pit with leafy materials to conserve soil moisture and maintain
optimum temperature.
Manuring
Apply cattle manure or compost at 10-15
t/ha as basal dressing. A fertilizer dose
of 80:60:80 kg of
N:P2O5:K2O per ha has to
be applied in two splits; half dose of N, full
P2O5 and half of
K2O within a week after sprouting; remaining half N and half
K2O one month after the first application along with
weeding and earthing up. Plant protection
Yam scale is found to infest the
corms both under field and storage situations.
Trailing
Trailing is essential to expose the
leaves to sunlight. Trailing has to be done within
15 days after sprouting by coir rope
attached to artificial supports in the open areas or
to trees where they are raised as an intercrop. When grown in open areas, trail to a
height of 3-4 m. Trail the vines properly as and when side shoots are produced.
Harvesting
The crop becomes ready for harvest within 8-9 months after planting when
the vines are completely dried up. Dig out the tubers without causing injury.
It is grown in a similar agro-climatic situation as that of D. alata. Planting season and manuring are also similar.
Varieties
(1) Sree Latha: This is a selection
from Thiruvananthapuram district with a duration of 8 months. Tubers are oblong to
fusiform with creamy white flesh. Vines twine to
the left.
(2) Sree Kala: This is an early variety
with 7.5 months duration. The tubers have 35-37 per cent dry matter, 23-25 per
cent starch and 1-1.3 per cent sugar.
Seeds and sowing
Select medium size tubers weighing
about 100-150 g each. Plant the whole tuber, one in each mound and cover completely
with soil. Mulch the mounds to maintain optimum temperature and moisture. To plant one
hectare 1800-2700 kg of seed materials
are required. Preparation of land
Plough or dig the land to a depth of
15-20 cm. Prepare mounds at a spacing
of 75 cm x 75 cm incorporating cattle manure
@ 1 kg per mound.
Manuring
The fertilizer dose and schedule
of application are the same as that of D. alata.
Trailing
Trail the vines by fixing small
poles attached with coir rope and direct 4-6
plants per pole. Harvesting
The crop is ready for harvest by about
7-8 months time. Tuber yields of 20-25 t
ha-1 can be obtained by following the improved methods of cultivation.
White yam or African yam is a new
crop species of edible yam introduced from Nigeria.
Varieties
Sree Subhra: The tuber contains 27-28 per cent dry matter, 21-22 per cent starch and 1.8-2 per cent protein. It is drought tolerant with 9-10 months duration.
Sree Priya: The tuber contains 25-27
per cent dry matter, 19-21 per cent starch and 2-2.5 per cent protein. It is drought
tolerant and duration is 9-10 months. It is suitable for inter-cropping in mature coconut garden
and with banana.
Manuring
FYM 15 t ha-1 to be applied at the
time of land preparation followed by application of NPK fertilizers @ 100:50:100 kg
ha-1. Full dose of P fertilizer along with 50 per cent of N and K fertilizers to be applied as
basal when 50 per cent of the planted setts sprouts. The balance 50 per cent of N and K
fertilizers to be applied as top dressing, 1 month after
the basal dressing which could be
combined with intercultural operations.
Rapid seed yam production
(minisett technique)
Sree Dhanya: It is the first dwarf variety. The tubers have 28-30 per cent dry
matter, 22-24 per cent protein and 0.3-0.5 per
cent sugar.
In this method clean and healthy yam
tubers weighing about 1 kg are cut
into cylindrical (disc-like) pieces, each about 5 cm thick. From each such piece, 2-4
small pieces (30 g) could be obtained by cutting the disc longitudinally or along the
two perpendicular diameters. Such a piece is called a "minisett". The minisetts are then spread out under light shade for an
hour with cut surface facing up before planting them in the nursery seedbeds. The
minisett takes 2-3 weeks for sprouting. At this stage, they are transplanted to the main
field at a spacing of 50 cm on ridges taken
1 m apart.
Sweet potato requires a warm humid tropical climate with a mean temperature of about 22 ºC. Though sensitive to frost, it can also be grown in the hills up to an altitude of 1500-1800 m as a summer crop. Under rainfed conditions the crop requires a fairly well distributed annual rainfall of 75-150 cm. Being a photosensitive crop, sunny days and cool nights are favourable for better tuber development. The crop can be grown on a variety of soils having good drainage, but grows best in fertile sandy loam soils. Heavy clayey and very light sandy soils are not suitable for proper tuber development.
Season
Rainfed crop: June-July, September- October
Irrigated crops: October-November
(for uplands) and January- February (for low lands)
Varieties
Improved varieties: H-41, H-42,
Sree Nandini, Sree Vardhini, Sree Rethna, Sree Bhadra, Kanjanghad, Sree Arun,
Sree Varun and Sree Kanaka.
H-41 _ Variety with excellent
cooking quality, sweet tubers and duration of 120 days.
H-42 _ Variety with excellent
cooking quality, sweet tubers and duration of 120 days.
Sree Nandini _ Early maturing,
drought tolerant variety with 100 - 105 days
duration and suited as catch crop in paddy fallows.
Sree Vardhini _ Early maturing,
carotene rich variety for food and feed with a
duration of 100 - 105 days. Sree Varun highly palatable varieties.
Sree Kanaka _ Short duration (75 -
85 days) variety with very high carotene (8.8 - 10 mg/100 g).
Kanjanghad _ KAU variety obtained through selection and duration of 105 -
120 days
Local varieties: Badrakali
Chuvala, Kottayam Chuvala, Chinavella,
Chakaravalli, Anakomban.
Sree Rethna _ Early maturing, carotene rich orange fleshed variety with 90 -
105 days duration.
Sree Bhadra _ Early maturing, (90 days), trap crop for nematodes.
Sree Arun Early maturing, (90 days),
Seeds and sowing
Sweet potato is propagated by means
of vine cuttings. To obtain vine cutting, raise nurseries from selected tubers using
the following method. Eighty kg of medium sized weevil free tubers (each of 125-150 g)
are required for planting in the primary nursery area (100
m2 to plant one hectare).
Plant the tubers at a spacing of 30-45
cm on ridges formed at 60 cm apart and replant in secondary nursery of about 500
m2 area at a spacing of 25 cm. Apply urea 15
days after planting at 1.5 kg / 100 m2 in the
primary nursery. To ensure better plant growth in the secondary nursery, 5 kg of
urea has to be applied in two split doses on
15th and 30th day after planting. Vines
obtained from the freshly harvested crop are also planted in similar nursery area to
obtain sufficient planting material. Cuttings
obtained from the apical and near apical portions
of the vines are preferable for planting in the main field. Storing of cut sweet potato
vines with intact leaves, in bundles covered with banana leaves (dipped in water) and
kept under shade for two days prior to planting is recommended. Irrigate the nursery
every alternate day during the first 10 days and
once in 10 days, thereafter. Vines will be ready for planting on the 45th day.
In the main field, plant vine cutting of
20-25 cm length on ridges 60 cm apart and at a spacing of 15-20 cm between the vines.
The cuttings can also be planted on mounds taken at a spacing of 75 cm x 75 cm. On the top
of each mound, 3-6 cuttings can be planted. Plant the vine cuttings with the middle portion
buried deep in the soil and the two cut
ends exposed to the surface. Ensure sufficient moisture in the soil for early
establishment of the cutting. Provide adequate drainage
and prevent water logging. Land Preparation
Make the soil to a fine tilth by
ploughing or digging to a depth of 15-25 cm. Make ridges 25-35 cm high, 60 cm apart
for planting vines. Manuring
Apply cattle manure or compost at
10 t ha-1 at the time of preparation of
ridges. The recommended
N:P2O5:K2O dosage
for sweet potato is 75:50:75 kg ha-1. For the reclaimed alluvial soils of Kuttanad,
the recommendation is 50:25:50 kg/ha. Apply N in two equal split doses, the first at the
time of planting and the second 4-5 weeks after planting. Apply full dose of
P2O5 and K2O at the planting time.
Irrigation
When grown as irrigated crop,
provide irrigation once in 2 days for a period of
10 days after planting and thereafter once
in 7-10 days. Stop irrigation 3 weeks before harvest. But one more irrigation may be
given 2 days before harvest. IW / CPE for higher tuber yield in non-rainy periods is
1:2 (approximate interval of 11 days). The application of N and
K2O at the rate of
50 kg/ha is recommended for the crop
grown under irrigation.
Aftercultivation
Conduct two weeding and earthing
up operations about 2 weeks and 5 weeks after planting. The top dressing of fertilizers
may be done along with the second
aftercultivation. Prevent development of small slender
tubers at the nodes by turning the vines
occasionally during active growth phase.
Rotation and mixed cropping
Under irrigated conditions, sweet
potato can be rotated with rice and planted during December-January after harvest of
the second crop of rice. As a mixed crop,
it can be grown along with
colocasia, elephant foot yam etc. Under rainfed conditions, green manure crops such
as kozhinjil and sunnhemp can be grown after harvest of the sweet potato and
later incorporated into the soil at the time of
land preparation for the succeeding crop.
Plant protection
Integrated control of sweet potato weevil
a) Remove and destroy the crop
residues of the previous crop.
b) Use healthy and weevil-free planting
materials. d) Trap adult weevils using sweet
potato pieces (of about 6 cm diameter) of 100 g size, kept at 5 m apart during 50 to
80 DAP at 10 days interval. Tubers may be cut and kept inside wire cages to
avoid rat damage.
e) Use pheromone traps (3Z dodecenyl
2E butenoate).
c) Apply Chromolaena odorata leaves as mulch @ 3 t
ha-1 at 30 DAP.
Harvesting
The duration of the crop depends on
the variety; but in general, the crop can be harvested in about 3.5 _ 4 months
after planting. Harvest the crop when leaves begin to turn yellow and the tubers mature.
The maturity of tuber can be ascertained
by cutting fresh tubers. The cut surface will dry clear if the tuber is mature and
becomes dark green if immature. Harvest the crop
by digging out the tubers without
causing injury.
Tapioca grows and produces best
under warm humid tropical conditions where
rainfall is well distributed and fairly abundant. It
can also be grown under irrigation where rainfall is low. Its outstanding characteristic in
terms of moisture requirements is the ability to withstand fairly prolonged periods of
drought. However, at the time of planting there
must be sufficient moisture for the plant to establish itself. The crop cannot
withstand cold and is killed by frost.
The crop grows well in well-drained laterite, gravelly and sandy loam soils.
Heavy and rocky soils are less suitable because they restrict root development. The crop
cannot survive waterlogged conditions and in such areas, it must be planted on mounds or
ridges that permit drainage. The crop can also be gown on hill slopes and on wastelands of
low fertility.
Season
The main planting seasons are
April-May with the onset of southwest monsoon and September-October with the onset of
north-east monsoon. Planting can also be done during February-April, provided
sufficient moisture is made available through
irrigation. For maximum tuber production, April-May
planting is preferred because the crop
can effectively utilize both the monsoons. The second best season is September-October. Varieties
H-97: This is a semi-branching variety, tolerant to mosaic disease with duration
of 10 months. But the harvest can be prolonged even up to 16 months. The starch content
is 30 per cent.
H-165: This is a non-branching type
with poor cooking quality having eight months duration. It is tolerant to mosaic
but susceptible to wilt disease. The starch content is 24.5 per cent.
H-226: This is a semi-branching type
with medium cooking quality having 10 months duration. It is moderately susceptible
to mosaic. The starch content is 29 per cent.
M-4: This is an erect type with
excellent cooking quality having 10 months
duration. The starch content is 29 per cent.
Sree Visakham: This is a
semi-branching type with yellow coloured flesh having 10 months duration. It shows high
tolerance to mosaic and low susceptibility to pests
like red mites, scale insects, thrips etc. The
starch content is 26 per cent and vitamin A 466 IU.
Sree Sahya: This is a predominently semi-branching type with 10 months
duration. It shows high tolerance to mosaic and
low susceptibility to pests like red mites, scale insects, thrips etc. The starch content is
30 per cent.
Sree Prakash: This has seven
months duration and the yield potential is 30-40 t
ha-1.
Kalpaka: This is a non-branching
type with six months duration and is suited as an intercrop of coconut in reclaimed alluvial
soils of Kuttanad.
Sree Jaya: This is an early variety
with seven months duration and excellent cooking quality. Tuber contains 24-27 per cent
starch and is low in cyanogens. Sree Vijaya: This is an early variety with 6-7 months duration and excellent
cooking quality. Tuber contains 27-30 per cent
starch and is low in cyanogens. Sree Harsha: This has 10 months duration and good cooking quality. Tuber contains
34-36 per cent starch. They are non-bitter and ideal for culinary purposes and the
high starch content makes it suitable for
preparing dried chips.
Nidhi: This is a high yielding early
variety with 5.5-6 months duration. It is tolerant
to mosaic and moisture stress. Tuber contains 26.8 per cent starch and 20 ppm HCN.
Vellayani Hraswa: High yielding
early variety with 5-6 months duration. It cannot tolerate drought. The cooking quality is
very good. Tubers contain 27.8 per cent starch and 53 ppm cyanogen.
Sree Rekha: It is a top cross hybrid with 10 months duration. Tubers contain
28.2 per cent starch with excellent cooking quality.
Sree Prabha: It is a top cross hybrid
with 10 months duration. Tubers contain 26.8 per cent starch with good cooking quality.
Seeds and sowing
Tapioca is propagated from
cuttings. Select mature healthy stems free from diseases or pests. Discard about 10 cm
from the lower mature and about 30 cm from the upper immature end. Stems should be
cut into setts of 15-20 cm length using a sharp knife. About 2000 stems are required
for planting one hectare. Harvested stems are to be stored vertically in shaded and well-aerated places. Spraying
dimethoate (0.05 per cent) on the stem will control
scale insects. Pit, flat, ridge or mound method of
planting can be adopted depending upon soil type, topography of land and elevation so
that waterlogging is avoided. Pit followed by mound is found to be the best method
of planting. Plant the cuttings vertically after smoothening the lower cut end, at a
depth not exceeding 4-6 cm. Adopt square method of planting at a spacing of 90 cm x 90 cm
@ one cutting per pit. It is preferable to adopt 75 cm x 75 cm spacing for
non-branching varieties like M-4.
Gap filling should be done within 15
days after planting preferably with longer setts
of 40 cm length. Sree Visakham is a choice variety recommended as an intercrop
in coconut gardens. Optimum plant population is 8000 plants per ha with 90 cm x 90
cm spacing.
Land Preparation
Before planting, plough the field 2-3
times or dig to a depth 25-30 cm depending upon soil type to establish a deep porous field
in which the setts are to be planted.
Minisett planting technique for
quality planting material Select an area with well drained soil
and irrigation facility. Shade net house of
35 per cent shade is ideal for the
germination and growth of minisetts. Mark out the
length and breadth and make raised beds of soil
: sand mixture in equal proportion. The beds could be of
convenient length and width not exceeding 1 m. An area of 220
m2 nursery is required for producing minisetts for
planting one hectare of land. Two node cuttings
are planted end to end horizontally, about 5 cm deep inside the soil, with the buds
facing either sides. Tip cuttings and four node
top setts should be planted erect at 5 cm x 5 cm spacing to prevent decay due to
excess moisture in these tender parts. Minisetts would sprout in a week's time. Mosaic
virus infected plants, if any found, should be
rogued off as soon as such symptoms are expressed, to keep the nursery disease free.
The minisetts will be ready for transplanting in about three to four weeks time. After
the basal application of recommended manure in the main field, ridges of 30 cm height
are taken with a spacing of 45cm between the ridges and planting is done on the ridges at
a spacing of 45 cm. Multiplication ratio by this process is enhanced to 1: 60 as against
the traditional method 1:10.
For producing minisetts, mature, disease free stems preferably those obtained
from indexed meristem culture should be selected. Two node cuttings are taken from
these stems using a sharp hack-saw. Top one-third portion is usually discarded in the
traditional system, however in the minisett technique,
it is fully utilized. The tip of the stem (about 5 to 6 cm long) is carefully cut
without causing damage. For preventing
dehydration, it is advisable to place the tip cuttings in
water. The stem just below the growing tip is very tender with prominent axillary buds.
Hence, from this portion, cuttings with four nodes are taken instead of two as the latter
may easily get dried up.
Preparation of nursery:
Manuring
Cattle manure or compost may be
applied at 12.5 t ha-1 during the preparation of
land or while filling up the pits so as to provide about 1 kg of organic manure per plant.
Apply fertilizers
N:P2O5:K2O at the rates (kg
ha-1) shown below:
H-97 and H 226 : 75:75:75 Sree Sahya:
M-4 and local: 50 :50 : 50
H-165, Sree Visakham, 100:100:100
N and K2O may be applied in three
split doses, i.e., 1/3 basal, 1/3 two months after planting and 1/3 three months after
planting. Dose of P2O5 can be reduced to half
where the crop is grown for more than 3 years
under full dose of recommended fertilizers, since under such situation there would be build
up of soil P.
For August-September planted
tapioca, apply half N, full
P2O5 and half K2O
basally with first digging and weeding. The
remaining quantity of N and K2O may be applied
45 days after planting at the time
of intercultivation.
In the acid soils of Kerala, 50
per cent of K requirement can be substituted by NaCl.
Note:
N:P2O5:K2O at 50:50:100 kg
ha-1 is recommended for Sree Visakham when grown as an intercrop in
coconut garden. Higher levels of N tend to increase HCN content of the tubers.
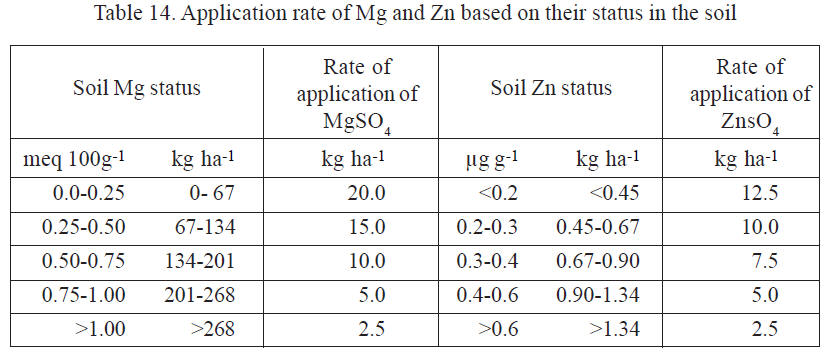
Soil application of Mg as
MgSO4 @ 20 kg ha-1 (1.62 g/plant) and Zn as
ZnSO4 @12.5 kg ha-1 (1g/plant) in small
channels around the mounds within 2 months of planting cassava providing an interval of
2 weeks between the application of
these fertilizer enhances tuber yield and quality. When they are used continuously,
their application rates can be fixed based on
their status in the soil following the table given below:

Aftercultivation
Keep the field free of weeds and
maintain soil loose by 2-3 shallow diggings or
hoeing upto 90 days after planting followed by
light earthing up. Retain two shoots on each plant in opposite directions and remove
excess shoots about 30 days after planting.
Irrigation
Under conditions of
well-distributed rainfall, tapioca grows well as a rainfed
crop and irrigation is not necessary. However, the crop has to be irrigated to provide sufficient moisture under conditions of prolonged
dry periods after planting. When the crop is grown under irrigation, yield increase of
150-200 per cent over the rainfed crop
has been observed.
Furrow irrigation with 25 mm water
at 100 mm CPE and alternate furrow irrigation with 50 mm water at 75 mm CPE
require only less water and labour for optimum
yield. Approximate irrigation interval schedules
will be 27 and 20 days respectively in summer months.
Intercropping in tapioca
Tapioca is planted at a spacing of 90
cm x 90 cm and it takes about 3-3.5 months time to have enough canopy to cover the land.
So it is possible to have an intercrop
of groundnut during the early stages of tapioca crop. Bunch varieties like TMV-2,
TMV-7, TG-3, TG-14 and Spanish improved are preferred for intercropping in tapioca.
The best season for sowing groundnut is May-June. Immediately after planting of
tapioca setts, groundnut seeds are sown at a
spacing of 30 cm between rows and 20 cm within rows, so that two rows of groundnut can
be accommodated in between two rows of cassava. A seed rate of 40-50 kg
ha-1 is recommended for dibbling one seed per
hill. Only well-matured and bold seeds are to be selected for sowing. In acid laterite soils
of Kerala, apply 1000 kg ha-1 of lime as basal dressing. A basal dose of 50:100:50
kg N:P2O5:K2O per ha should be given
uniformly to both the crops. One month after
sowing of the seed, 20 kg each
P2O5 and K2O and 10 kg N /
ha-1 may be given to the intercrop along with earthing up. Once pod
formation has started (i.e., 40-45 days after
sowing) the soil should not be disturbed, as it will
affect the pod development adversely. The groundnut crop matures in 105 to 110
days. After the harvest of pods, the haulms are incorporated in the soil along with a
top dressing of 50 kg each of N and K2O per
ha for the main crop. By adopting this practice, 20-25 per cent additional income can
be obtained.
In sandy areas intercropping tapioca
with cowpea / groundnut / black gram / green gram may be recommended giving a spacing of
20 cm on both sides of the ridges. The
non-trailing grain cowpea variety V-26 is
recommended as a companion crop along with tapioca.
For a pure crop of tapioca or for a cropping system
involving tapioca as the main crop and
the pulse crop suggested above, the field may be irrigated once in 36 days to a depth of 5
cm. This recommen-dation is for shallow water table situations. For deep water
table situations, the crop may be irrigated once
in 24 days to a depth of 5 cm.
Plant protection
Cassava mosaic disease (CMD)
The disease is transmitted by a white fly
Bemisia sp. As a rule, only stem cuttings from disease free plants should be used
for planting to minimize the spread of the virus disease. For this purpose, tagging of
disease free healthy plants for selection as
planting materials must be practised from
September to December. All plants showing even
very mild symptoms must be rejected. Mosaic tolerant varieties such as H-97 may be
used to minimize economic loss of tubers.
Production of disease free planting material of tapioca through
nursery techniques
Setts of 3 to 4 node cuttings
from apparently disease free plants are collected and planted in the nursery at a very
close spacing of 4 x 4 cm so that about 500 setts can be accommodated in one square
metre land. Daily watering of the setts has to be done for the first 10 days and on
alternate days afterwards. Screening of CMD symptoms may be started 10 days
after planting. Setts showing even mild symptoms are to be removed and burnt. This must
be continued up to 20-25 days, by that time healthy seedlings can be transplanted to
the main field. Supplementary irrigation may be given in the transplanted field till they
get established. Screening for disease symptoms and roguing of infested plants may
be continued in field at weekly intervals upto harvest. The selected healthy stems are
again cut into minisetts and subjected to nursery and field screening. By adopting
this technique it is possible to produce healthy plants.
Leaf spot
Spray 0.2 per cent zineb or 1 per
cent Bordeaux mixture for control of leaf spot.
Bacterial blight
Bacterial blight is a disease noted
in severe proportion in certain parts of Kerala. Chemical control is not effective. Use
of resistant or tolerant varieties is the only method of control. Among improved
varieties, H-97, H-226, H-1687 and H-2304 are tolerant to the disease while H-165 is
highly susceptible. Among the local varieties,
M-4, Paluvella, Pichivella, Parappilppan, Anamaravan etc. are tolerant to the disease.
Red spider mites and scale insects
Red spider mites in the field and
scale insects under storage are important pests of tapioca. Under field conditions
light infestation of mites can be controlled effectively by spraying the crop with water
at 10 days interval from the onset of
mite infestation. In the case of very severe infestation, the crop can be protected
by spraying 0.05 per cent dimethoate at monthly intervals from the time of appearance
of mites. The stem may be sprayed with 0.05
per cent dimethoate before storing as a prophylactic measure against the scales. Termites
To control termites infesting planted
setts, sprinkle a little of carbaryl 10
per cent or chlorpyrifos in the mounds prior to planting.
Management of storage pests of cassava
Treating chips with granular salt (3
per cent), sun drying thoroughly and storing in gunny bags in godown are very
effective against Araecerus fasciculatus
and Sitophilus oryzae.
Harvesting
Tapioca becomes ready for harvest
9-10 months after planting. Hybrid varieties like H-226, H-97 and H-165, when grown
under recommended management practices have recorded yields up to 40-50 t
ha-1 of raw tuber.
COLEUS (Solenostemon rotundifolius)
Coleus thrives well in tropical and subtropical regions. A well-drained medium fertile soil is suitable for its cultivation.
Season
Plant the cuttings in the main field between July and October.
Variety: Nidhi, Sree Dhara and Suphala.
Sree Dhara _ First variety in chinese potato with good cooking quality and 5
months duration.
Nidhi _ Variety released from RARS, Pattambi with 5 months duration.
Suphala _ A tissue culture mutant derived by KAU from local cultivar suited for year round cultivation with a duration of 120 - 140 days.
Nursery
Raise the nursery approximately one month before planting. An area of 500 to 600 m2 is sufficient to produce cuttings required for one ha of main field. Apply 125 to 150 kg FYM in the nursery area. Plant the seed tubers at a spacing of 15 cm on the ridges taken 30 cm apart. About 170 to 200 kg of tubers is required to raise the nursery. Take the vine cutting to a length of 10-15 cm from the top portion after three weeks from planting.
Preparation of main field
Plough or dig the land to a depth of 15-20 cm and form ridges 30 cm apart or raised beds of 60-90 cm width.
Planting
Plant the vine cutting collected from the nursery on ridges at a spacing of 30 cm or on raised beds at 30 cm x 15 cm spacing.
Manuring
Broadcast 10 tonnes of FYM and N:P2O5: K2O @ 30:60:50 kg ha-1 and incorporate into the soil at the time of land preparation. Topdress with N and K2O at the rate of 30 and 50 kg ha-1 respectively at 45 days after planting.
Aftercultivation
Give weeding and earthing up, at 45 days after planting along with topdressing. Cover a portion of the vine with soil to promote tuber formation.
Plant protection
To control the root-knot nematode,deep plough the field in summer, adopt crop rotation and destroy root residues and other plant parts by burning.
Harvesting
Harvest the crop 5 months after planting.
Citation:
Kerala Agricultural University. 2011.
Package of Practices Recommendations: Crops.
14th Edition. Kerala Agricultural University, Thrissur. 360p.