AD HOC RECOMMENDATIONS FOR MANAGEMENT OF
SECONDARY AND MICRO NUTRIENTS
A. CROP-WISE RECOMMENDATIONS:
1. Rice
Preventive strategies for Zn management
• Presoak seeds in a 2 % ZnSO4 suspension in water (20 g ZnSO4 per litre). 1kg seed to be presoaked in 1 litre of ZnSO4 suspension for 24 hours, drain and keep for sprouting.
• Fertilizer management: Apply sufficient quantity of organic manure. Incorporate 20kg Zn sulfate per ha in the soil before seeding or transplanting.
Treatment of Zn deficiency
If Zn deficiency symptoms are observed in the field, apply 20kg ZnSO4 .7 H2O per ha. Foliar spray of 0.5% ZnSO4 solution,( 1kg ZnSO4 + ½ kg lime to avoid phytotoxicity in 200 L water ha-1 ie. 5g ZnSO4 + 2.5g lime per litre of water) for emergency treatment of Zn deficiency in growing plants. Apply at tillering (25–30 DAT), and give two or three repeat applications at intervals of 10–14 days. Application of magnesium as basal dose @ 20 kg MgO/ha is effective in giving significant increase in grain and straw yield of rice in magnesium deficient soils.
2. Coconut
Magnesium sulphate @ 0.5-1.0 kg/palm/year is recommended for root (wilt) affected area.
For sandy and sandy loams of Onattukara and similar situations and also for hybrid palms grown in root (wilt) affected areas, apply 500 g MgSO4/palm/year.
Apply lime or dolomite during April-May, magnesium sulphate during August- September and organic matter during May – June. For an adult palm 1 kg dolomite or 1 kg lime + 0.5 kg MgSO4 is required per annum.
3. Arecanut
Magnesium sulphate @ 60 g, borax and zinc sulphate @ 20 g per palm/year can be recommended for yellowing affected palms.
4. Ginger and Turmeric
Boron @ 2 kg/ha and Zinc sulphate @ 30 kg per hectare can be used in deficient soils.
5. Groundnut
Application of S and B @ 20 kg and 4 kg/ha respectively can be recommended.
6. Cowpea:
Lime @ 250 kg/ha or dolomite @ 400 kg/ha can be recommended at the time of first ploughing.
7. Cocoa
Dolomite @ 100 g/plant/year to plants from the third year onwards. In case of zinc deficiency, spray 0.5 to 1.5 % ZnSO4 three times a year.
8. Sesamum
Sulphur @30 kg.ha-1 and boron @2.5 kg. ha-1 is can be recommended for sesame in rice fallows of Onattukara. Apply Zn SO4 20 kg. ha-1 in the loamy/ sandy soils of Onattukara region in case of deficiency.
9. Black Pepper
When Soil pH < 5.5 – apply lime @ 500 g/ standard, in alternate years. Use Dolomite if Mg is also low. Apply 200g Mg SO4 per vine when there is Mg deficiency. In a zinc deficient soil, apply zinc sulphate @ 30g per vine ( 30 kg/ha ZnSO4) or give foliar spray of 0.5% Zinc sulphate twice at new flushing and spike initialization stage. In case B deficiency, apply Borax @ 10 to 20g/standard or give foliar spray of 0.2% borax. When there is Mo deficiency apply sodium molybdate @1 kg/ha or give foliar spray @ 0.1%.
10. Cardamom
In zinc deficient soils, apply zinc sulphate @ 25 kg/ha or give foliar spray of 0.25% Zinc sulphate twice at flushing and panicle initialization stage. Apply Borax @ 7.5 kg/ha in B deficient soils or give foliar spray of 0.2% borax.
11. Tomato:
Soil application @ 10 kg ZnSO4 ha-1 and 2 kg B ha-1 is recommended for tomato.
12. Rubber
In case of magnesium deficiency symptoms use 50 kg of commercial magnesium sulphate per hectare.
13. Cassava
In case of deficiency, use MgSO4 @ 20 kg/ha and ZnSO4@ 10 kg/ha, S @50 kg /ha S and B as borax @ 10 kg/ ha.
14. Sweet potato
In case of Boron deficiency use borax @1.5 kg ha-1.
B. SOIL BASED RECOMMENDATIONS:
In cases where crop-specific recommendations are not available, the following guidelines can be used for recommending secondary and micro nutrients.
Secondary Nutrients (Ca, Mg, S)
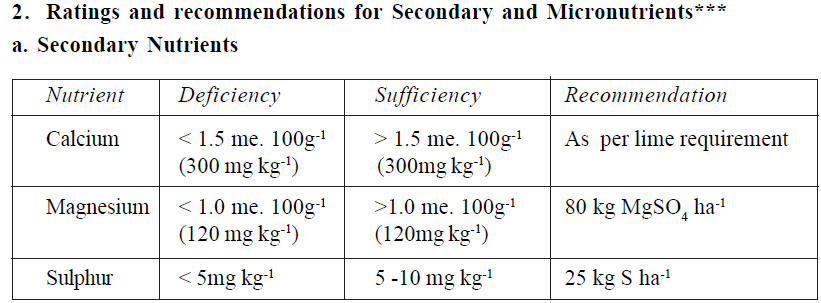
Calcium deficiency can be anticipated in extremely acidic, highly leached tropical soils. If the exchangeable Ca level is less than 300 mg kg-1, soils are classified as deficient. Lime application at rates given below is recommended.

Magnesium deficiency can also be observed under extremely acidic soil environment. If the exchangeable Mg level is less than 120 mg kg-1
, soils are classified as deficient. Application of MgSO4 @ 80 kg ha-1 is recommended.
Highly leached tropical soils may develop S deficiency. When available sulphur levels in soil are less than 5 mg kg-1, symptoms may appear. Application of sulphur/ sulphur containing fertilizers to give 25kg S per hectare is recommended.
Micro nutrients (Fe, Mn, Cu, Zn and B)
Kerala soils in general have high levels of iron and manganese. Toxic soluble levels of these elements can be managed by liming. Deficiency situation may arise in sandy soils with neutral/alkaline reaction. When the available Fe is less than 5 mg kg-1 the soil is considered as deficient. Application of FeSO4 @ 15 kg ha-1 is recommended. Available Mn level less than 1 mg kg-1 soil condition is rated as deficient. Foliar application of 0.5% MnSO4 is recommended.
Copper deficiency is observed in 31% of soils in Kerala. Available Cu level below 0.12 mg kg-1 in neutral / alkaline soils and below 1 mg kg-1 in acid soils is rated as deficient. Application of CuSO4.5H2O @ 2 kg /ha, seedling dip in 1% copper sulphate solution or soaking of seeds in 0.25% copper sulphate solution for rice is recommended .
Deficiency of Zn is observed in about 34% soils in Kerala. Available Zn less than 0.6 mg kg-1 in neutral/alkaline soils and 1 mg kg-1 in acid soils is rated as deficient condition. Application of ZnSO4.7H2O @ 20 kg ZnSO4 ha-1 is recommended. Foliar application of 3 kg ZnSO4 dissolved in 187 litres of water per hectare, 20-25 days after planting is recommended for rice.
Deficiency of B is observed in highly leached soils. Available B levels less than 0.5 mg kg-1 in soil can be rated as deficient. Deformation of young leaves, drying/withering of growing points, failure in splitting of leaflets in coconut, chocking etc are some of the symptoms. Application of 10 kg Borax ha-1or 0.5% solution of Borax as foliar spray is recommended.
Where ever crop specific ad hoc recommendations are not available, general recommendations as indicated in the table attached can be adopted. These ad hoc recommendations can be used to combat problems of deficiency/excess of secondary/micro nutrients until further refinements and modifications are made.
1. NPK ratings and recommendations for field crops (Fertilizer recommendations on area basis)